Note: This web page is a part of DTSC's Hazardous Waste Classification training course.
Corrosive Wastes
![]()
Corrosive wastes1 are acidic or alkaline (basic) wastes that can readily corrode or dissolve materials they come into contact with.
We measure corrosivity by either pH or the rate of steel corrosion:
pH: When aqueous solution has a pH less than or equal to 2, or greater than or equal to 12.5, it is considered corrosive.
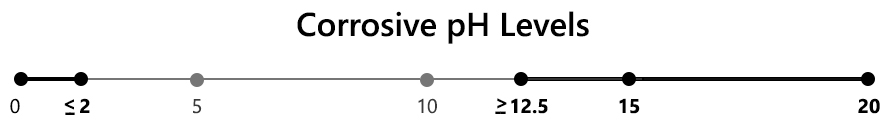
When a non-aqueous solution mixed with an equal weight of water has a pH of less than or equal to 2 or greater than or equal to 12.5 it is considered corrosive. See exclusion for cementitious materials.
Corrosivity test: US EPA, SW-846, 3rd edition, Method 9040.
Rate of Steel Corrosion: When a liquid corrodes steel (SAE 1020) at a rate greater than 6.35 mm (0.250 inch) per year at a test temperature of 55°C (130°F), it is considered corrosive.
If a non-liquid, when mixed with an equal weight of water, corrodes steel at a rate greater than 6.35 mm per year, it is considered corrosive.

Rate of Steel Corrosion test: US EPA, SW-846, NACE Standard TM-01-69.
Corrosive wastes (liquids only ) are listed under RCRA waste code D002.
California’s characteristics for corrosive hazardous waste is slightly different than the federal RCRA system. RCRA only recognizes corrosive liquids while California also includes corrosive solids.
In California, to determine whether a solid would exhibit the corrosive characteristic, one would mix the solid with an equivalent weight of water and testing the pH of this non-aqueous solution. If the pH was less than or equal to 2 or greater than or equal to 12.5, this solid waste would be a non-RCRA hazardous waste.
References
1 22 CCR section 66261.22
2 US EPA SW-846, 3rd edition, Method 9040
Q5: Characteristics of Haz? Section Links
Hazardous Waste Classifications Training Links
Connect / Contact Us
Office Locations / Map
Sign up for an E-List
Regulatory Assistance Officers
Statewide Campaigns/Alerts
Report an Environmental Concern
Amber Alert
California Grants Portal
Register to Vote
Save Our Water.com



 Katherine M. Butler, MPH
Katherine M. Butler, MPH